This article contains information customized for NerdWallet members. Not a member yet?
This article contains information customized for NerdWallet members. Not a member yet? Sign up today for a free credit score and see how NerdWallet can help you make all the right money moves.
When you check your credit score, you’ll probably want to know what the three digits mean and find out how you compare. What is a good credit score?
VantageScore 3.0 and FICO 8, the most commonly used credit scoring models, have a range of 300 to 850. Each lender sets its own standards for what constitutes a “good” score. But, in general, scores fall along the following lines:
Credit score ranges
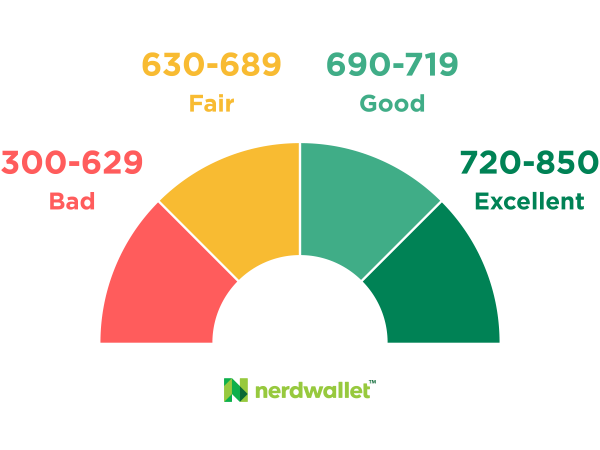
- Bad credit, in the 300-629 range, can make it difficult to qualify for credit, leaving you with few good options when you need to borrow money.
- Fair credit, in the 630-689 range, gives you more options, but you'll likely pay higher interest and will have a limited choice of credit cards.
- Good credit, in the 690-719 range, can give you lower interest rates and more choices.
- Excellent credit of 720 and up can give you access to most rewards credit cards and the lowest interest rates offered.
For both VantageScore and FICO scores, the data used in calculating credit scores comes from the bureaus, and the most important factor is on-time payments. Because FICO and VantageScore consider much the same factors, a good score with one is predictive of a good score with the other.
Here’s how scores break down for the two main scoring systems:
FICO score ranges
Data from April 2018 show the average FICO score nationally was 704.Less than 20% of scores fell below 600; 22.6% were between 600 and 699, and 58.2% were 700 or above.
VantageScore ranges
The average VantageScore 3.0 was 680 in 2018, according to credit reporting agency Experian.Its 2017 data showed that 22.3% of Americans had VantageScores between 781 and 850, while 21.2% were below 600.
Get your score, know what powers it
Check your credit score for free. NerdWallet delivers personalized insights and updates your info weekly so you can see your progress. Get started — it's freeCheck your credit score for free. NerdWallet delivers personalized insights and updates your info weekly so you can see your progress.
How does your credit score affect your life?
VantageScore was developed by the three major credit bureaus — Equifax, Experian and TransUnion — to compete with FICO, the credit scoring algorithm used for the majority of lending decisions in the United States. Most FICO scores also range from 300 to 850, and the higher the score, the better. (Some versions of the FICO score, such as those for the auto and credit card industries, are on different scales.)For both VantageScore and FICO scores, the data used in calculating credit scores comes from the bureaus, and the most important factor is on-time payments. Because FICO and VantageScore consider much the same factors, a good score with one is predictive of a good score with the other.Here’s how scores break down for the two main scoring systems:Data from April 2018 show the average FICO score nationally was 704.Less than 20% of scores fell below 600; 22.6% were between 600 and 699, and 58.2% were 700 or above.The average VantageScore 3.0 was 680 in 2018, according to credit reporting agency Experian.Its 2017 data showed that 22.3% of Americans had VantageScores between 781 and 850, while 21.2% were below 600.Even if your score is in the low 500s, you may still be able to get credit, but it will come with very high interest rates or with specific conditions, such as depositing money to get a secured credit card. You may have to pay more for car insurance or put down deposits on utilities.
As you add points to your score, you’ll have access to more credit products.
But as you add points to your score, you’ll have access to more credit products — and pay less to use them.
For instance, someone with FICO scores in the 620 range would pay $65,000 more on a $200,000, 30-year mortgage than someone with FICOs over 760, according to data gathered by Informa Research Services.
» MORE: Is your credit score high enough to to get a decent car loan?
At the other end of the scale, borrowers with scores above 750 or so have many options, including the ability to qualify for 0% financing on cars and 0% interest credit cards.
Find the starting point
It’s important to know where you stand, so it pays to monitor your score. You can get a free credit score from a number of personal finance websites, including NerdWallet, which offers VantageScore.
The important thing is to use the same score every time you check. Doing otherwise is like trying to monitor your weight on different scales — or possibly switching between pounds and kilograms. Some sources may be using a different scale entirely.
Pick a score and stick with it to track improvement.
So, pick a score and stick with it to track improvement. Progress you make measured by one score will be reflected in the others. (Here’s how to bump up your credit; these methods apply to whatever score you decide to track.)
And be aware that, like weight, scores fluctuate. A score is a snapshot, and the number can vary each time you check it. As long as you keep it in a healthy range, those variations won’t have an impact on your financial well-being.
Lenders look at more than credit scores
When you go to borrow money, a good credit score does not guarantee a good interest rate — or even approval.
Credit scores look at your reported credit history to gauge the likelihood that you will repay borrowed money; you can be deep in debt and still have great credit scores if you have paid all your bills on time.
Your income and other debts play a key factor in some lending decisions, as lenders consider what you owe alongside what you earn and assets you have accumulated.
But your credit reports don’t reflect whether you can afford to repay the credit you are applying for. That’s why your income and other debts play a key factor in some lending decisions, as lenders consider what you owe alongside what you earn and assets you have accumulated. Lenders use a debt-to-income ratio calculation to evaluate whether you can repay a loan.
No comments:
Post a Comment